Anatomy of External ear
INTRODUCTION
The ear is an organ of hearing. It is also concerned with maintaining the equilibrium of the body One hears with the ears. The centre for hearing is in the temporal lobe of the brain above the ear
It consists of three parts:
- External ear
- Middle ear
- Internal ear
EXTERNAL EAR
Features of external ear :
external consist of ear pinna, the external acoustic meatus and external auditory canal and the tympanic membrane
AURICLE (pinna):
it is made up of a single plate of elastic cartilage which is lined with skin on both sides.
the lowest part of the auricle is the lobule, it is soft and made up of fibrofatty tissue.
the auricle is divided into different parts :
- helix
- anti-helix
- concha
- tragus
- scaphoid fossa
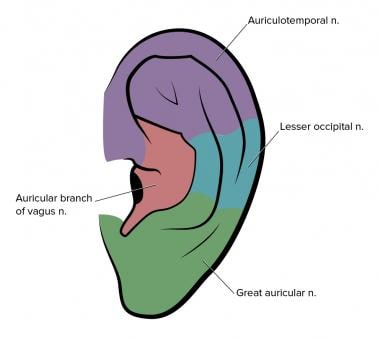
nerve supply :
Auriculotemporal nerve - upper 2/3rd of lateral surface
Great auricular nerve - lower 1/3 of lateral surface and medial surface
Lesser occipital nerve - upper two-thirds of the medial surface
Auricular branch of the vagus nerve - root of auricle
Facial nerve - auricular muscles
blood supply :
blood supply is through posterior auricular and superficial temporal artery
lymph drainage: the preauricular and postauricular lymph nodes
EXTERNAL ACOUSTIC MEATUS
features of external acoustic meatus :
- conducts soundwave from concha to the tympanic membrane.
- The canal is S-shaped
- 24 mm long
- 16 mm is bony (medial 2/3rd)
- The bony part is formed by the tympanic plate of the temporal bone
- 8 mm is cartilaginous (lateral 1/3 rd)
- it is filled with fibrous tissue
- the anterior wall and the floor are longer than the posterior wall and roof
- The narrowest point, the isthmus, lies about 5 mm from the tympanic membrane
- The lining skin is adherent to the perichondrium and contains hairs, sebaceous glands, and ceruminous or wax glands (modified sweat glands)
Outer part of canal - superficial temporal and posterior auricular arteries
Inner part of canal - deep auricular branch of maxillary artery
nerve supply :
aurictemporal nerve - skin in the anterior half of meatus
auricular branch of vagus - skin in posterior half
TYMPAIC MEMBRANE
features :
- thin and translucent
- 9 x 10 mm, oblique at an angle of 55 degrees
- OUTER SURFACE
- lined by thin skin
- it is concave
- INNER SURFACE
- has attachment to the handle of the malleus
- it is convex
- point of maximum convexity at the tip of malleus is called umbo
- the greater part of the tympanic membrane is tightly stretched is called the pars tensa.
- the part between the two malleolar folds is loose and is called the pars flaccida.
STRUCTURE :
tympanic membrane is composed of three layers :
1. outer cuticular layer of skin
2. middle fibrous layer
- made up of superficial radiating fibres and deep circular fibres. - The circular fibres are minimal at the centre and maximal at the periphery.
The fibrous layer is replaced by loose areolar tissue in the pars flaccida
3. inner mucosa layer
-lined by a low ciliated columnar epithelium.
blood supply :
outer surface - deep auricular branch of maxillary artery
inner surface - anterior tympanic branch of maxillary artery
- posterior tympanic branch of auricular artery
venous drainage:
outer surface - external jugular vein
inner surface - transverse sinus and venous plexus around the auditory tube
lymph drainage: preauricular and retropharyngeal lymph nodes
nerve supply:
- outer surface
- anteroinferior by auricuotemporal nerve
- posterosuperior by auricular branch of the vagus nerve
- inner surface
- tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve through tympanic plexus


Comments
Post a Comment