Nose anatomy
INTRODUCTION
the nose is the most prominent part of the face.
It is the opening for the respiratory pathway and it acts as an olfactory sensor in our body.
it contains various olfactory receptors and nasal sinus
the olfactory mucosa lines
the nose is divided into the following sections
- external Nose
- nasal cavity
- lateral wall of Nose
- conchae and meatuses
EXTERNAL NOSE
the external nose is further divided into
- root
- dorsum
- tip

bones in the nose:
- nasal bone - forms the nasal bridge
cartilages in nose :
- septa nasal cartilage
- lateral nasal cartilage
- major alar cartilage
- minor alar cartilage
- vomerovaginal cartilage
muscles in the nose:
- dilator naris
- depressor septi
- levator labi superiors alaeque nasi
the skin over external nose is supplied external nasal, infratrochlear and infraorbital nerve.
NASAL CAVITY
the nasal cavity extends from nostrils to posterior nasal aperture.
it is divided into right and left half
each half has a floor, roof, medial wall and lateral wall
roof:
- about 5 - 7 cm long
- has an anterior and posterior slope
- the anterior slope is formed by a nasal plate of the frontal bone
- posterior bone is formed by the inner surface of the sphenoid bone
floor:
- made by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine
- about 5 cm long
lateral wall:
- lateral walls contain concha
NASAL SEPTUM
it separates both nasal cavities
it contains both boney and cartilaginous part
boney part is formed by:
- vomer
- perpendicular part of the ethmoid
- frontal, sphenoid, palatine and maxillary bone contribute to the margins

cartilaginous part is formed by :
- septal process
- septal part of inferior nasal cartilage
cuticular part- fibrofatty tissue
the nasal septum is usually deflected
ARTERIAL SUPPLY
anterosuperior - anterior and posterior ethmoidal artery
anteroinferior - septal branch of superior labial artery
posterosuperior - sphenopalatine artery ( also called the artery of epistaxis)
the anteroinferior region has anastomoses of all the arteries that form a capillary network called kiesselbach's plexus
VENOUS DRAINAGE
anterior - facial vein
posterior - sphenopalatine vein
NERVE SUPPLY
1. General sensory nerves
they arise from the trigeminal nerve
- anterosuperior part -
- internal nasal branch of the
ethmoid nerve - posteroinferior part
- nasopalatine branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion
- olfactory nerves are confined to the upper part of the olfactory area
- the olfactory area contains olfactory mucosa
- the mucus protects the olfactory epithelium and allows diffusion of odour
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE
anterior half - submandibular nodes
posterior half - reterophyrageal and deep cervical nodes

LATERAL WALL OF NOSE
it contains shelf-like boney projections called conchae. they increase the surface area of air conditioning
the lateral wall separates the nose from
- orbit
- ethmoidal air sinus
- maxillary air sinus
- lacrimal sac
- nasolacrimal duct
it is divided into 3 parts
- vestibule - small depressed part in the anterior
- atrium - middle space
- conchae and conchae meatus
the lateral wall is partly cartilaginous and partly boney
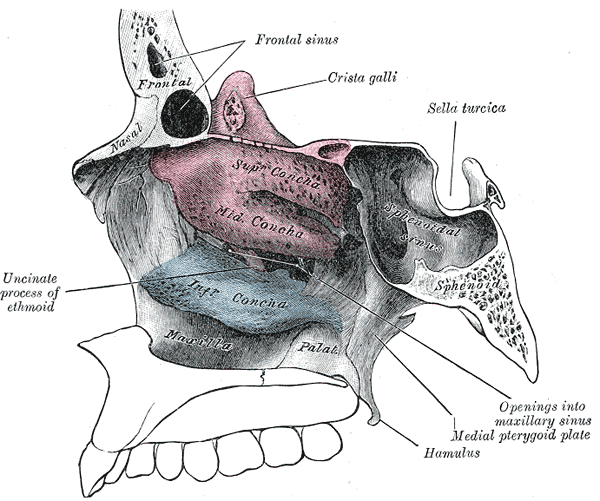
the boney parts are formed by
- nasal
- frontal process of the maxilla
- superior and middle nasal conchae (made from the labyrinth of ethmoid)
- inferior conchae formed by spongy bone
- palatine bone and their processes
cartilaginous part
- superior nasal cartilage
- inferior nasal cartilage
- cartilage of ala
the cuticular lower part is formed by fibrofatty tissue
CONCHAE
nasal conchae are boney projections that are present in the lateral wall
there are 3 conchas
- superior concha
- smallest concha
- situated above the posterior part of the middle concha
- middle concha
- from the medial wall of the ethmoid labyrinth
- inferior concha
- it is an independent bone
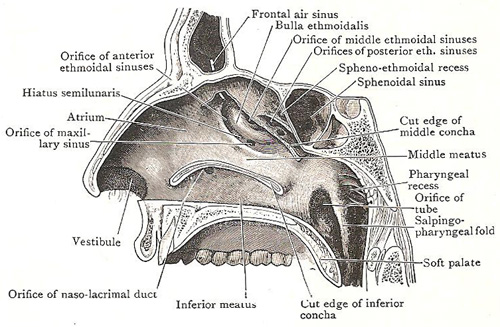
MEATUS
meatus of the nose is the passage below the conchae
1. inferior meatus
- the largest meatus
- nasolacrimal duct opens in the middle
- the opening is guarded by lacrimal fold or hasners valve
2. middle meatus
- middle ethmoidal sinus opens at ethmoidal bulla
- ethmoidal bulla is a rounded prominence
- the infundibulum is a short passage below the meatus
- hiatus semilunaris is a deep semicircular sulcus below bulla
- frontal air sinus opens in the anterior part
- ethmoidal air sinus opens behind frontal sinus
- maxillary sinus opens in the posterior part

3. superior meatus
- below superior concha
- receives opening of posterior ethmoidal air sinus
4. sphenoethmoidal recess
- triangular fossa above superior concha
- opening of sphenoidal air sinus
5. Atrium of the middle meatus
- a shallow depression in front of the middle meatus
ARTERY SUPPLY
anterosuperior quadrant - anterior ethmoidal artery
anteroinferior quadrant - facial artery
posterosuperior quadrant - sphenopalatine artery
posteroinferior quadrant - great plalatine artery
veins from plexus to drain into
- facial vein
- pharyngeal plexus
- pterygoid plexus
NERVE SUPPLY
1. general sensory nerves
- anterosuperior quadrant - anterior ethmoidal nerve
- anteroinferior quadrat - anterior superior alveolar nerve
- posterosuperior quadrant - posterior superior nasal branch from pterygopalatine ganglion
2. special sensory nerves
- upper part of the lateral wall
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE
- drained by submandibular, retropharyngeal and deep cervical node




Comments
Post a Comment