ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD
INTRODUCTION
the spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system.
it contains the pathways that carry information from and to the brain.
tracts that carry sensory information to the brain are called ascending tracts
tracks that carry motor information from the brain to muscles are known as descending tracts
FEATURES
lies in the vertebral canal.
it extends from the foramen magnum to the lower border of the first lumbar vertebrae
it is covered by bone, meninges ( dura matter, arachnoid matter, pia mater ), cerebrospinal fluid.
the space between the spinal cord and the spinal dural sheet is called Epidural space
cauda equina - a collection of long descending nerve roots present in the lower portion of the vertebral canal (filum terminal)
the spinal cord has 2 enlargements
- cervical enlargement
- innervates upper extreme areas
- lumbar enlargement
- innervates lower extreme areas

- cervical 8
- thoracic 12
- lumbar 5
- sacral 5
- coccygeal 1

- Anterior median fissure
- Posterior median sulcus
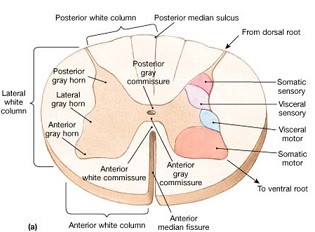
- anterolateral sulcus
- lateral to the anterior median fissure
- exit for anterior nerve root
- posterior median septum
- posterior intermediate septum
- posterolateral sulcus
- anterior funiculus
- contains the anterior spinothalamic tract
- posterior funiculus
- contains the fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cutnaeous
- lateral funiculus
- contains lateral spinothalamic tract

- Ascending tracts - carries the sensory impulse to the brain
- descending tracts - carries motor impulse to the motor units
- transverse tract - communication between the one side of the spinal cord and the other side
- Anterior (ventral) horn
- contains cell bodies of somatic motor neuron
- alpha motor neurons - supplies the skeletal muscle
- gamma motor neuron - supplies proprioceptors (position) in muscle
- interneurons regulate the activity of the alpha motor neuron
- they are the largest at cervical and lumbar region
- Lateral horn
- preganglionic fibres of the sympathetic division (internal organ) of ANS
- prominent in the thoracic, lumbar and sacral segments
- they supply visceral organs
- axons leave the spinal cord through the anterior (ventral) root
- the ventral root contains both somatic and autonomic fibres
- posterior (dorsal) horn
- contains fibres of afferent track neurons that carry the sensory impulse
- the cell bodies of the sensory neuron are present in the enlarged region of the dorsal root called dorsal root ganglion
- the axons entering the posterior horn can ascend or synapse with interneuron in the posterior horn
- posterior horn has several layers
- substantial gelatinosa of rolando
- nucleus of proprius
- clarke's column
- visceral afferent nucleus

Comments
Post a Comment